Data-driven Decision Making Powered by E-receipt Data
In an era where data-driven decision making and business intelligence are becoming increasingly important, businesses and investors are perpetually seeking faster ways to gauge what is going on in the market and how to better position themselves for success. One way to achieve this is to leverage alternative data sources such as e-receipts data.
In this article, we will explore how e-receipt data can be utilized to help further business intelligence or facilitate the investment process when it comes to arriving at predictions.
What is E-receipt Data?
First things first, what is e-receipt data? ‘E-receipt’ is short for electronic receipt and is simply real purchase data collected from transactional email receipts. From tracking purchase trends, basket composition, inventory levels, making informed sales forecasts, optimizing online stores, and making smarter investment decisions, e-receipt data has proven to be an accurate data source for extracting deeper consumer insights and for forecasting revenues.
Unlike credit card and POS data though, panel size and available data for evaluation for e-receipts is typically smaller since the collection process requires an opt-in system or rewards app. Nonetheless, e-receipt data is largely accurate at tracking retail revenue so can be confidently utilized as a means to conduct revenue forecasting and to better understand the customer journey from a transactional data point of view.
Advantages and Drawbacks of E-receipt data
One of the major advantages of e-receipt data is the level of granularity offered and the longer period of complete history. This contrasts with credit card data, which, while more commonly used due to its accessibility and large amount of volume, only offers one merchant name and the amount of dollars spent at that particular merchant as a whole. Item-level information, purchase patterns, consumer behavioral trends and demographic information will not typically be available.
For example, owing to the granularity of e-receipt data, email receipt data can be used to deduce metrics such as an average item’s cost rather than just the average amount spent by customers. Such level of detail in data really aids organizations who conduct extensive consumer research and are willing to invest in consumer insights and business analytics.
That said, there are limitations of e-receipt data. Namely, they cannot capture in-person purchases from brick-in-mortar stores that don’t send e-receipts.
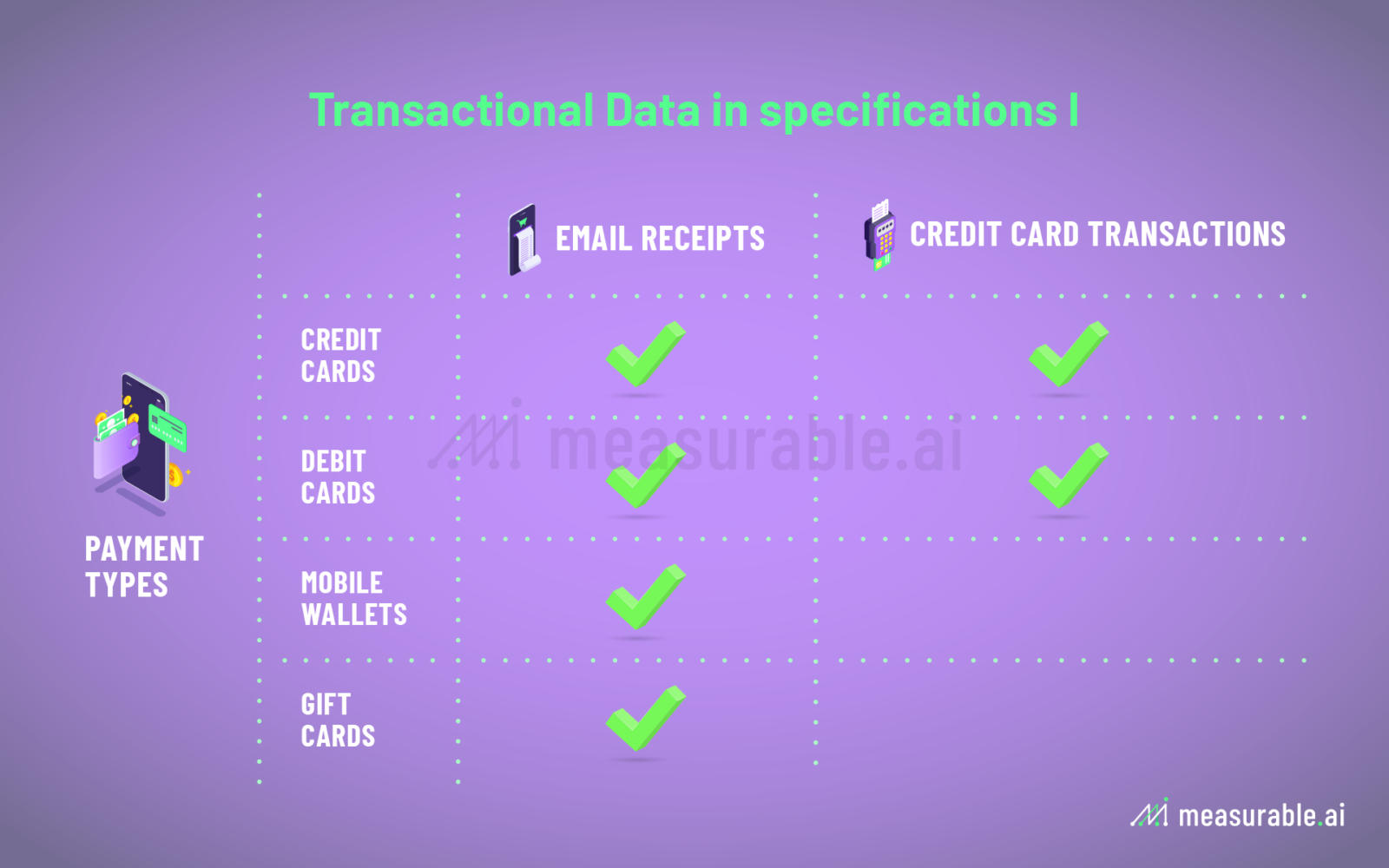
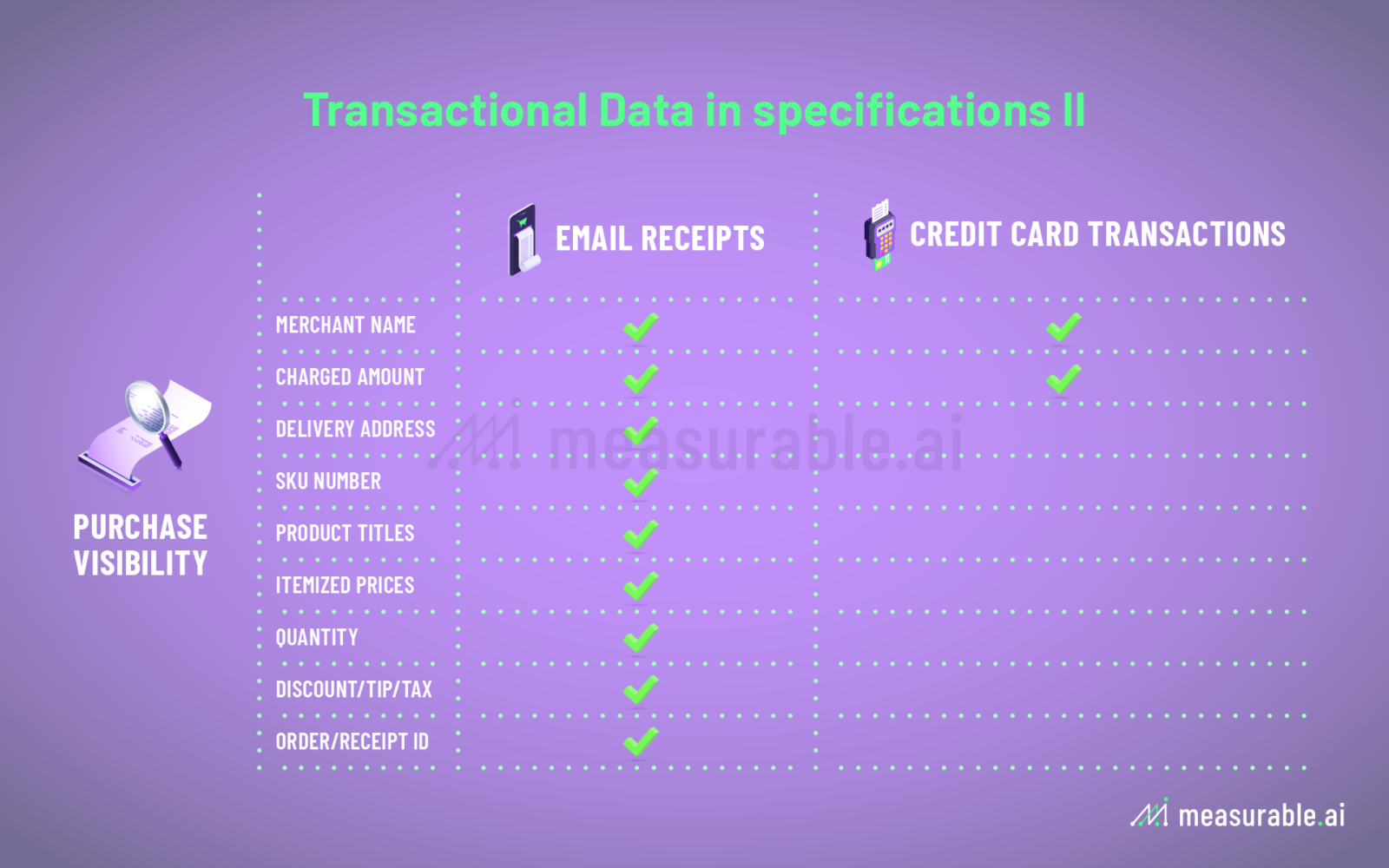
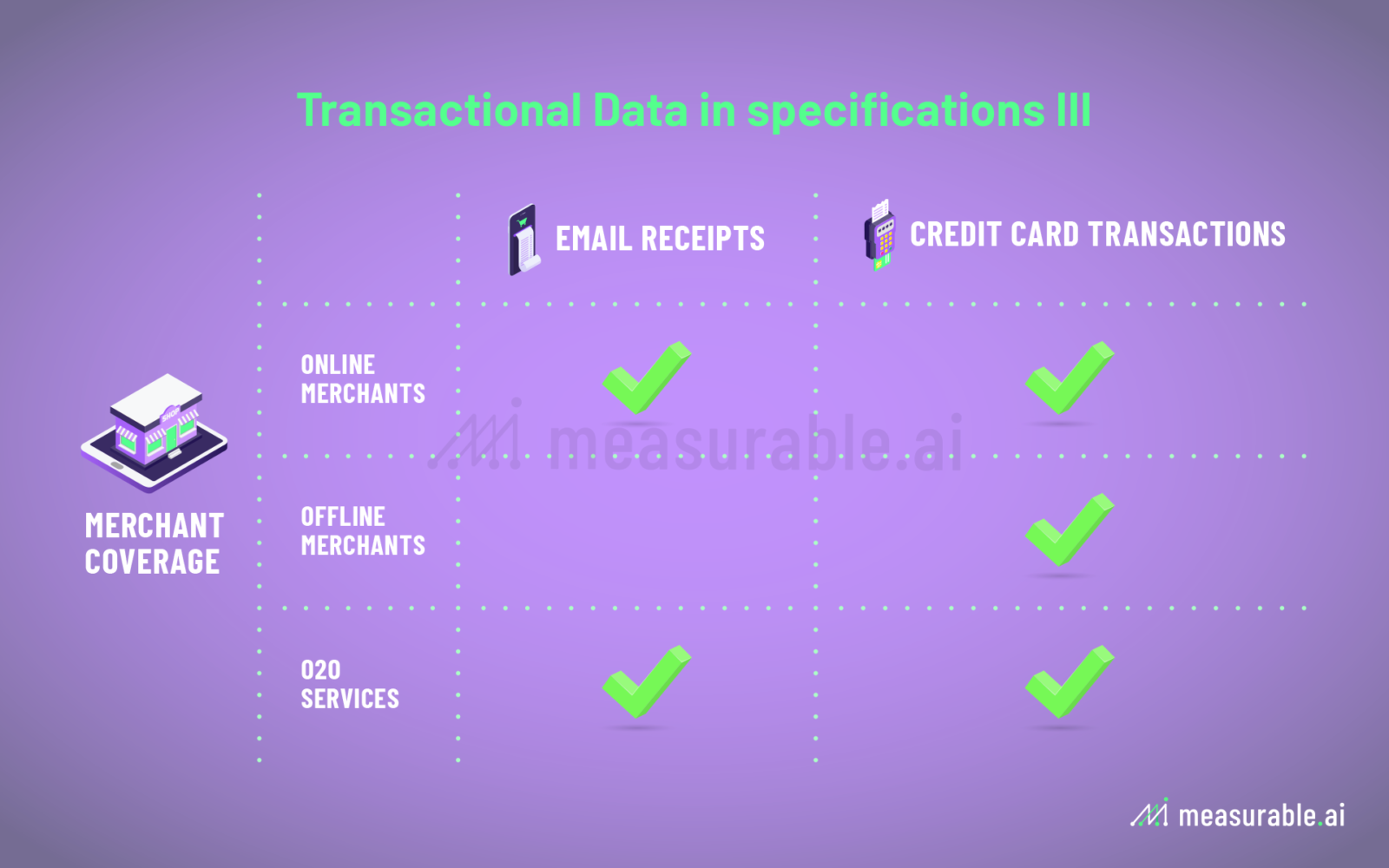
How is E-receipt Data Collected and What can be Captured?
You may be wondering, how do firms even attain e-receipt data? Often it is collected through an email software the end-user has installed. An automated scraper is coded to extract information from transactional emails only, bypassing all personal emails. The data is then anonymized and aggregated to remove any personal identifiable information (‘PII’). Sometimes the data is further structured into different categories (e.g. SKU of the product(s) purchased, time and date of the transaction, geolocation data, country transaction took place, and payment method used).
As to what data fields can be extracted from an e-receipt, you can take a look at the below examples.

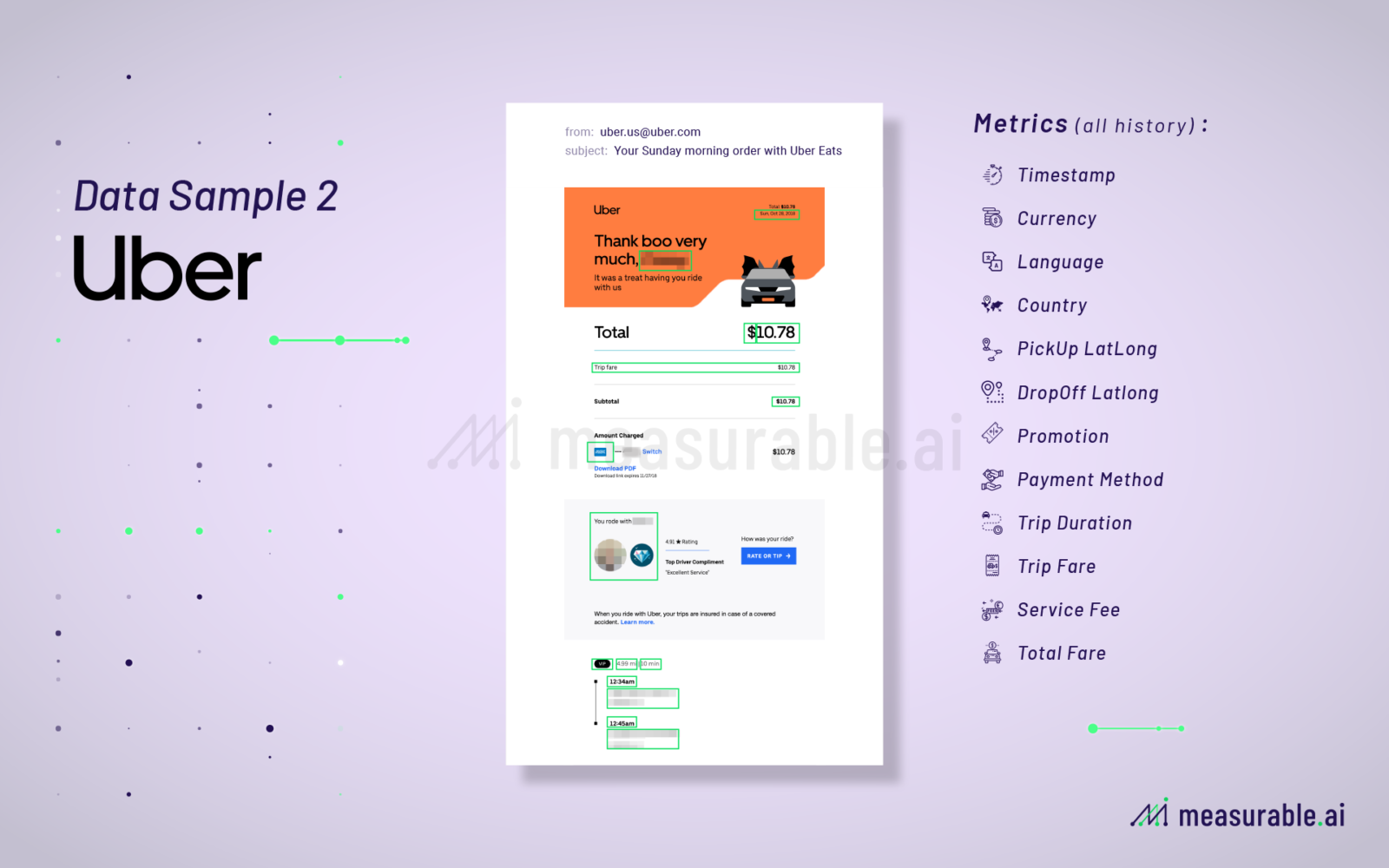
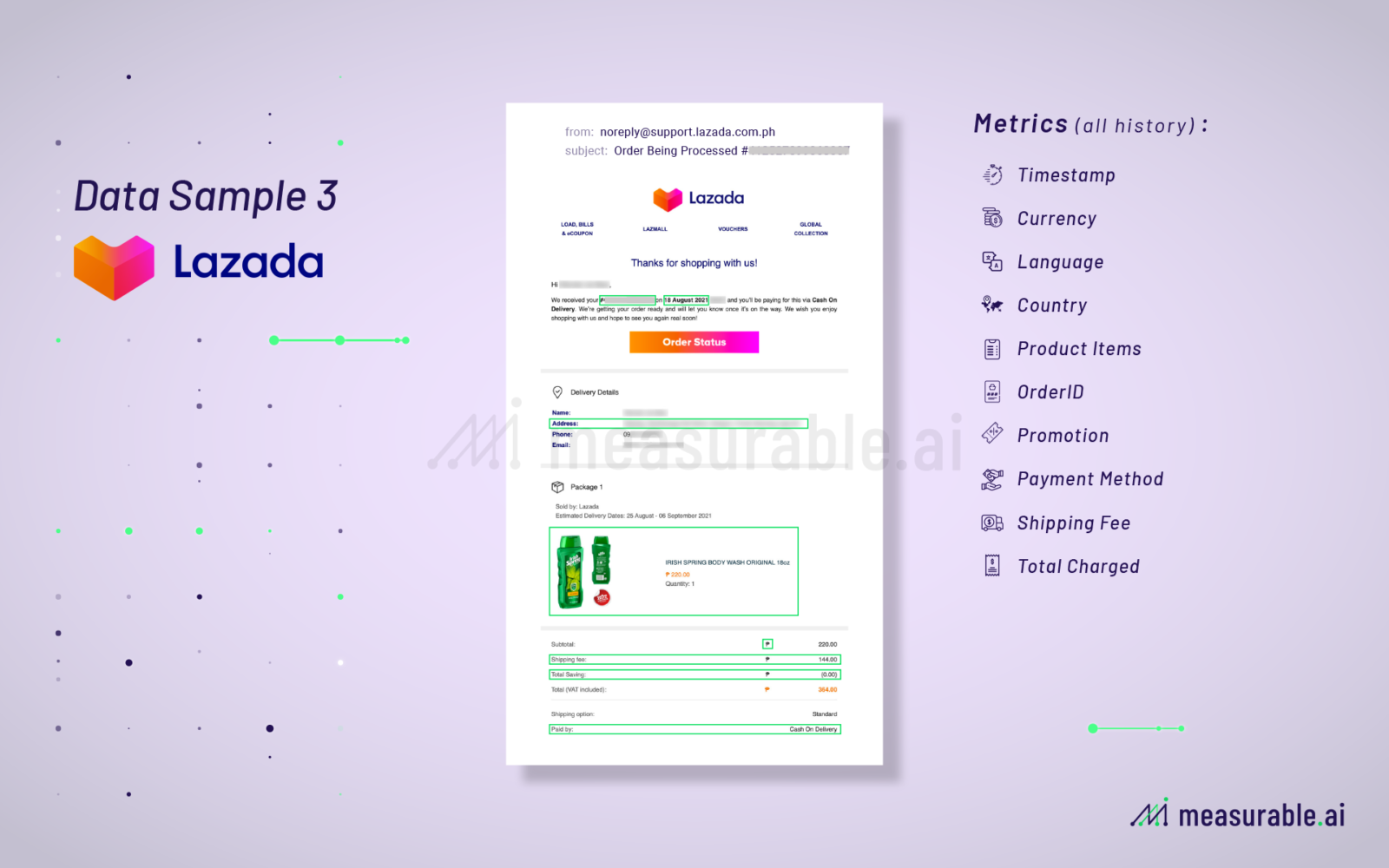
Typical fields captured are customers name, seller’s name, the product or service that has been paid for, the quantity of products purchased, the amount paid, payment method used, the date of transaction, and the time of transaction.
How to Use E-receipt Data
E-receipt data is predominantly used by corporations and investors for commercial intelligence and forecasting power respectively.
Businesses of all sizes can benefit from utilizing data from e-receipts, and many investment firms are leveraging on e-receipts as an alternative data source to forecast sales figures and calculate market share.
From startups, consumer goods companies, consultancies, to Fortune 500 companies, businesses of all sizes and across multiple industries can all stand to benefit from the intelligence gathered from e-receipts. Some common use cases are listed below:
- To understand customer purchasing behavior better
- Gain better clarity as to how consumers respond to different products in the market and see at what times their sales peak
- See which sellers are driving the most revenues
- Observe how products perform relative to their peers
- Sharpen marketing strategies and customer loyalty programs
- Forecast demand and expected revenue plus identify profitable investment opportunities
E-Receipt Data for Forecasting
One of the most common use cases of our e-receipts data is to serve as a proxy of companies’ revenues and sales.
At Measurable AI, we have backtested our data against reported revenues and orders as well as analysts’ consensus estimates as reported by Bloomberg. For illustrative purposes, below is a sample of backtested data on Etsy.
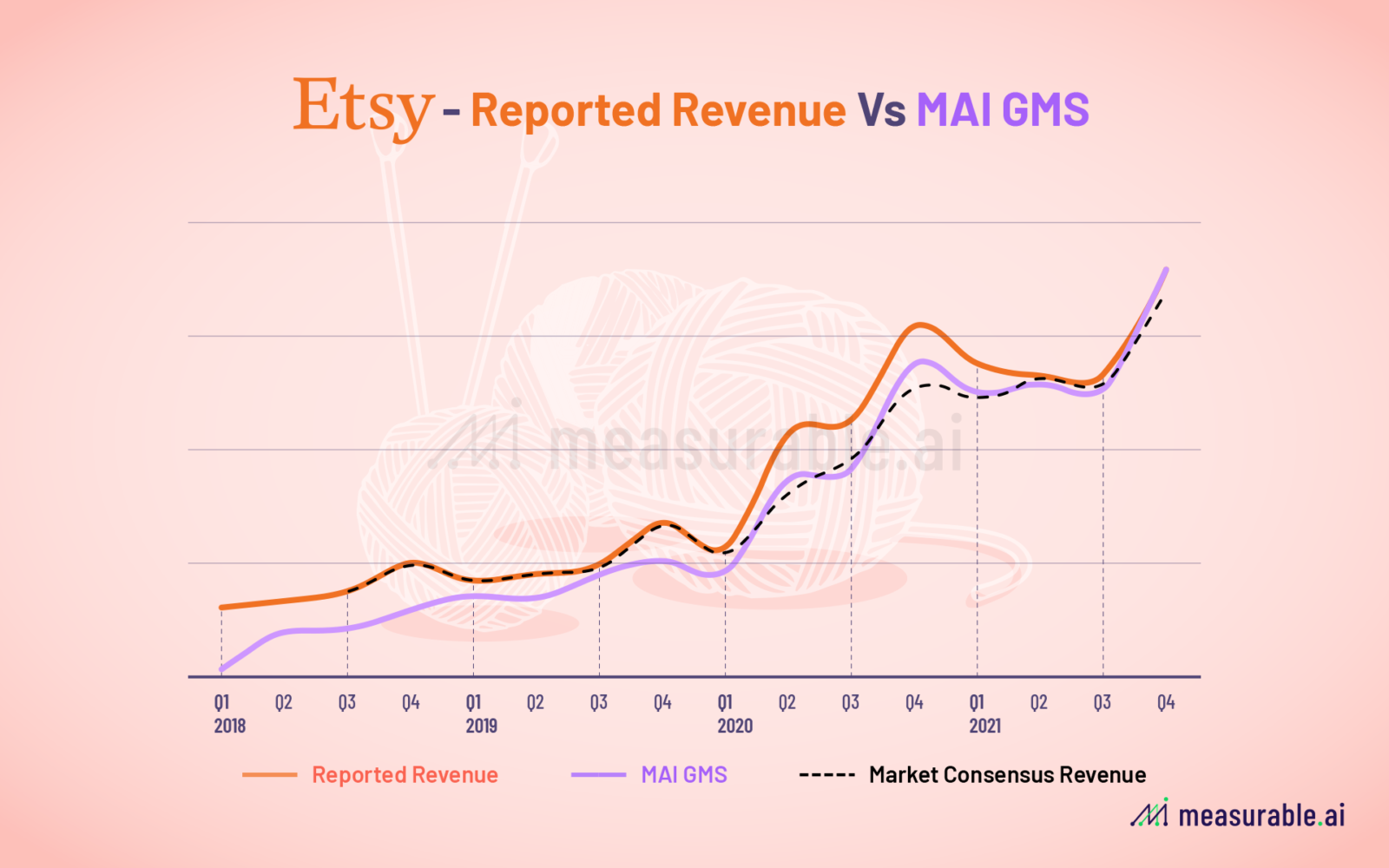
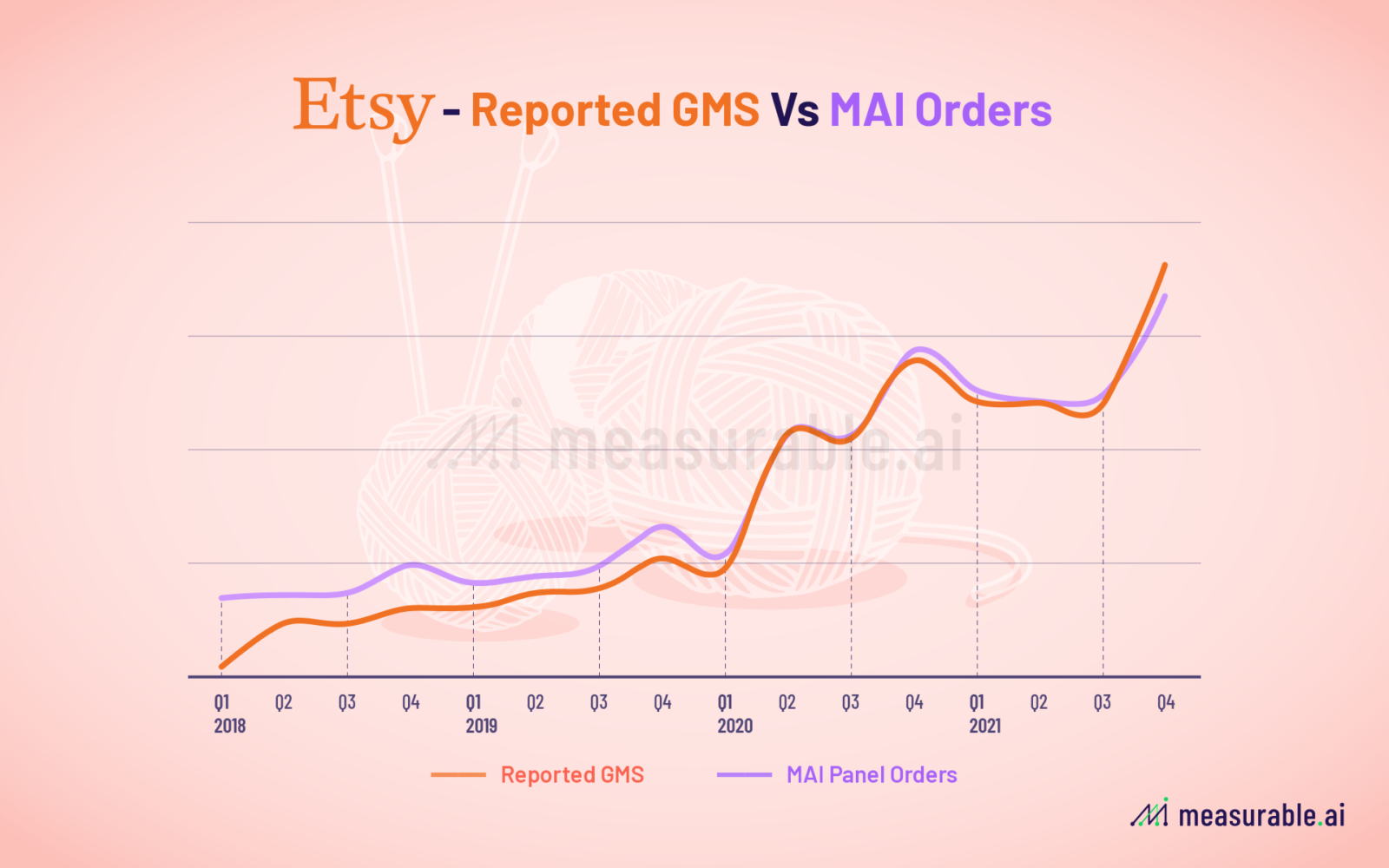
A benefit of using the email receipts dataset is that the investors can generate predictions swiftly following the quarter’s end as all sample data is updated on a weekly or daily basis with information syncing in almost real time.
For more details about our backtesting results and companies covered, please contact us at [email protected].
About Us
Michelle Tang is a Managing Director at Measurable AI who specializes in digital marketing and strategic partnerships with a passion for data analytics and consumer intelligence. She enjoys research and storytelling with insights derived from Measurable AI’s very own e-receipts data.
You can reach her at [email protected].
Measurable AI is the leading granular e-receipt provider for consumer intelligence in the emerging markets with a core focus in South East Asia, Middle East, India and Latin America. Major sectors covered are ride hailing, food delivery, e-commerce and digital payments.
![]()
